What makes CNG ‘green’?
Compressed Natural Gas is an environmentally clean alternative fuel that is the cleanest burning of all conventional fuels. CNG is composed of mostly methane and when burned during the combustion process, it produces carbon dioxide and water vapor which releases very minimal amounts of greenhouse gases.
While gasoline, diesel, and propane products produce higher amounts of carbon, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides (NOx) and reactive hydrocarbons which form ground-level ozone (main component in smog).
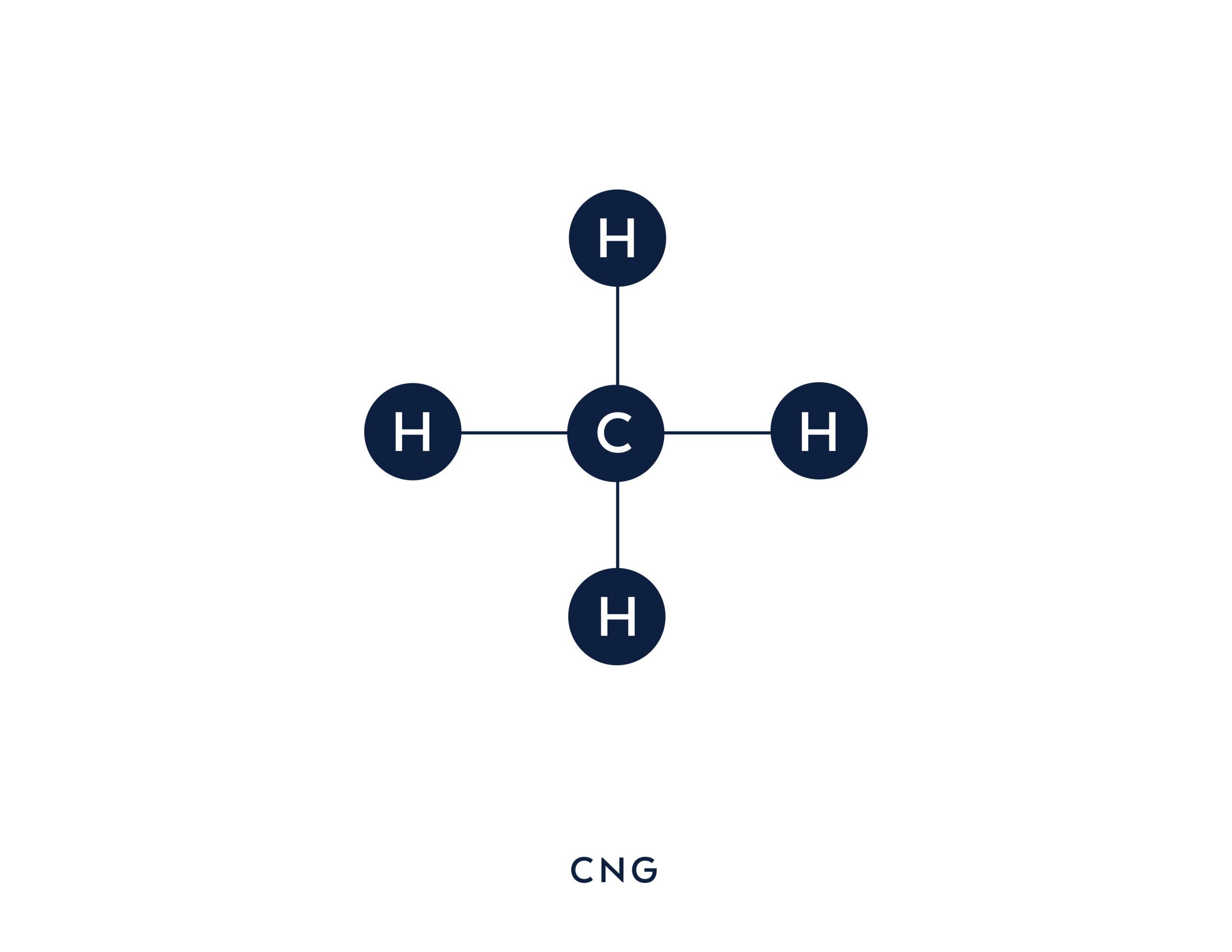
CNG’s low carbon footprint is the result of being primarily consisting of methane, or CH4. Methane is a ‘clean burn’ as it only has one (1) carbon atom accompanied by four (4) hydrogen atoms.
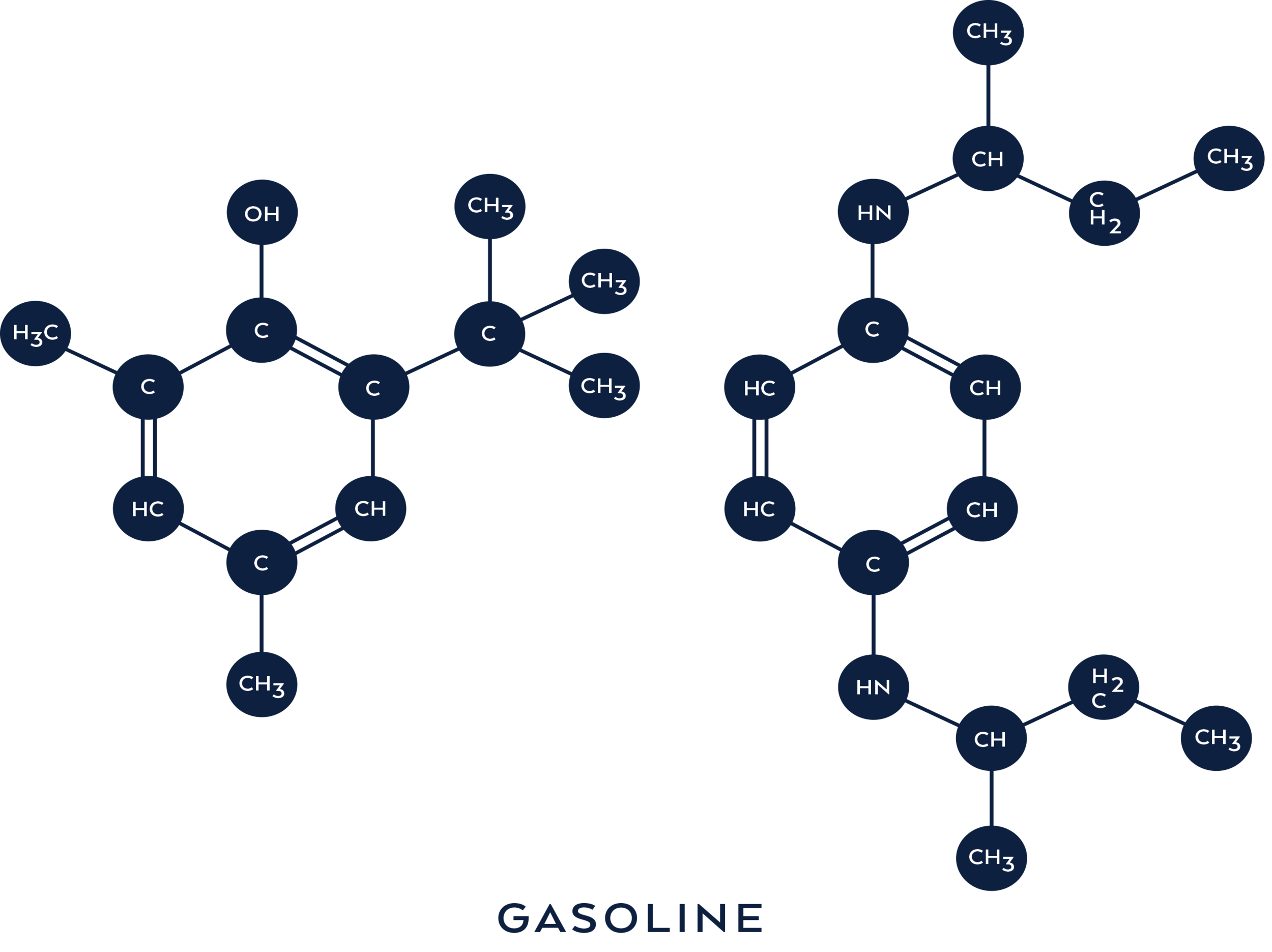
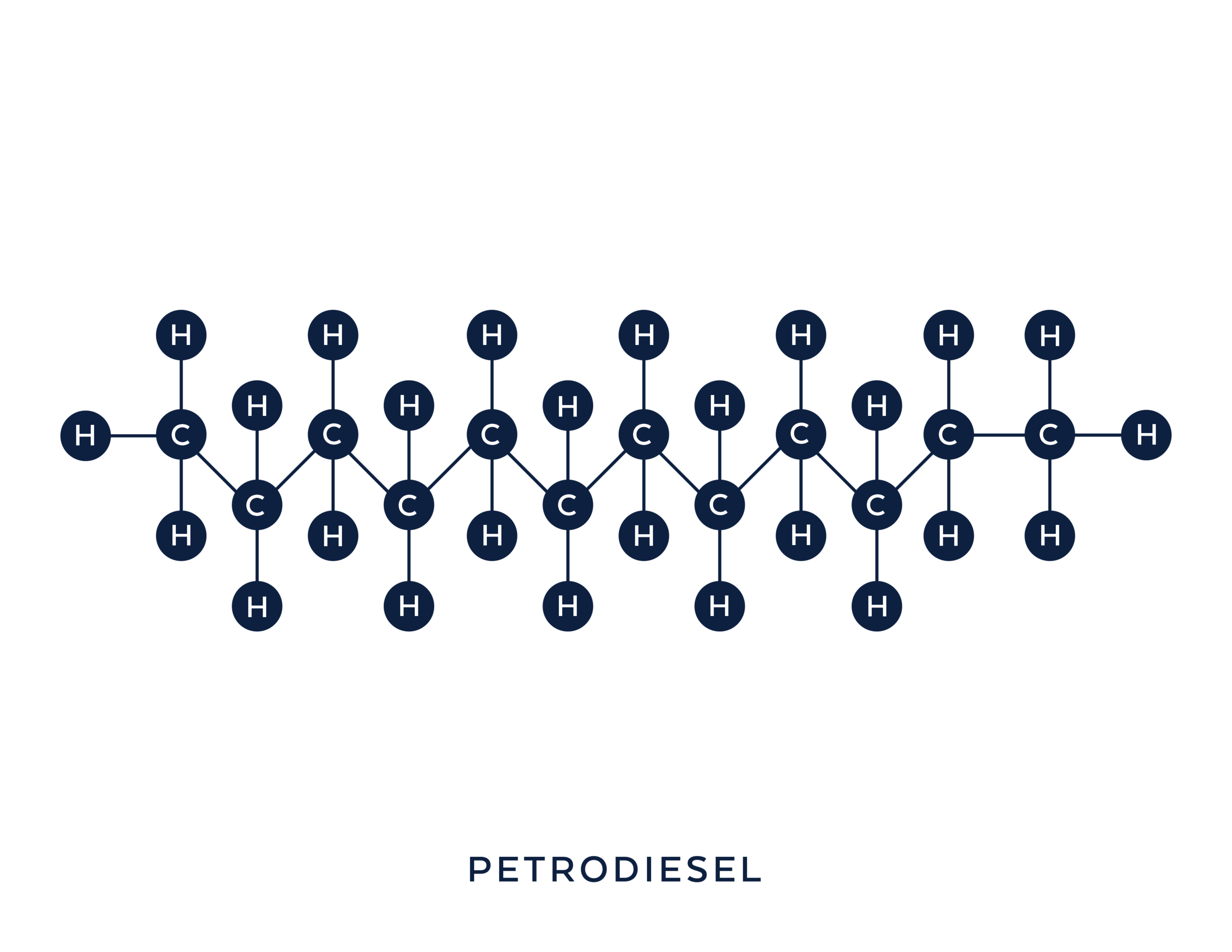
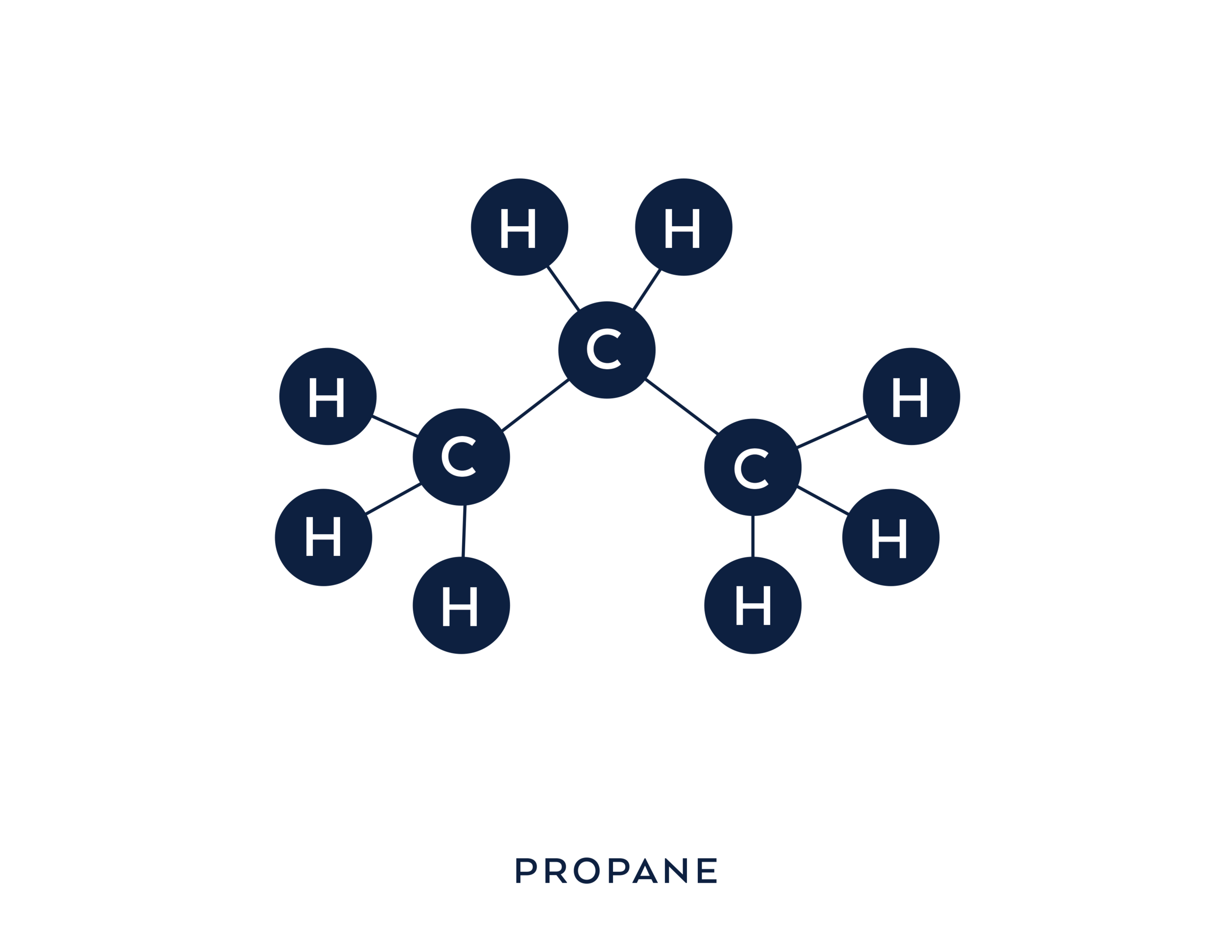
Compared to gasoline (C8H18 + 28 O2), which has eight (8) carbon atoms, diesel (C12H23), which is made up of 12 carbon atoms, and propane (C3H8) which is made up of three (3) carbon atoms.
Based on a natural gas study from the U.S. Department of Energy, light-duty Natural Gas Vehicles (NGV) emits 6-11% lower greenhouse gas (GHG) levels throughout the life cycle emissions benefits over conventional fuels.
When CNG is compared to LNG (liquid natural gas), they have similar life cycles however, CNG does emit fewer GHG.

Schools making the switch from traditional fuels to CNG for their transportation services are eligible to receive LEED credits for their school.
Additionally, school can also apply for State and Federal grants to assist with costs towards a greener future. Connect with us to learn more.
Other Benefits of CNG
Explore more benefits of using CNG in your district’s buses by clicking/tapping each button below.